NIH-funded researchers developed an online tool that can analyze self-collected, at-home videos with a smartphone. When deployed in a nationwide study, the tool could predict physical health and osteoarthritis of the knee or hip.

NIH-funded researchers developed an online tool that can analyze self-collected, at-home videos with a smartphone. When deployed in a nationwide study, the tool could predict physical health and osteoarthritis of the knee or hip.
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University are developing lipid nanoparticles that are designed to carry mRNA specifically to the pancreas. Their study in mice could pave the way for novel therapies for intractable pancreatic diseases, such as diabetes and cancer.
Researchers are developing new MRI contrast agents that are activated in low oxygen environments enabling improved diagnosis and treatment of hypoxic tumors as well as other diseases.
Bioengineers from Columbia University are developing a pipeline to systematically evaluate how bacterial treatments might synergize with existing anti-cancer therapies in preclinical models.
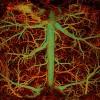
Scientists at Duke University supported with funds from NIBIB have developed an ultra-fast photoacoustic imaging system capable of visualizing functional and molecular changes in the brain related to major brain disorders.

After years of research, an NIH-funded team has developed a wearable cardiac ultrasound imager that can non-invasively capture real-time images of the human heart. The prototype patch, which is about the size of a postage stamp, can be worn during exercise, providing valuable cardiac information when the heart is under stress.

Using state-of-the-art imaging technology, NIH-funded researchers have found the secret behind the glassfrog’s ability to become transparent, an effective form of camouflage. Future research may provide insights into disorders related to blood clotting or stroke in humans.
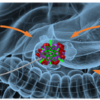
NIBIB-funded researchers are developing a new method to treat pancreatic cancer. In their study, they combined an injectable radioactive gel with systemic chemotherapy in multiple mouse models of the disease. The treatment resulted in tumor regression in all evaluated models, an unprecedented result for this genetically diverse and aggressive type of cancer.

NIBIB-funded researchers are fine-tuning a wearable, cuffless blood pressure monitor. Made of graphene, one of the thinnest materials in the world, the device is worn on the underside of the wrist and can measure blood pressure with comparable accuracy to a standard blood pressure cuff.

The National Institutes of Health has awarded research funding for seven pilot projects developing early stage, yet groundbreaking neuro-technologies. The innovative projects would enable new medical devices to diagnose and treat both acute and chronic disorders, from neuropathic pain to mental illness.